Effective Solutions for Receding Gums
Receding gums are a prevalent dental condition where the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth's root. This can lead to sensitivity, discomfort, and if left untreated, severe oral health issues.
Understanding the stages of gum recession and adopting effective preventative measures is crucial for maintaining good oral health. In this blog, we'll explore the causes, prevention strategies, and treatments for receding gums, providing you with expert advice to keep your smile healthy and beautiful.
What are receding gums?
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, occur when the gum tissue around the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth's root. This exposure can lead to increased sensitivity, especially to hot and cold, and makes the teeth more susceptible to decay, since the roots lack the protective enamel of the tooth crown.
This condition can also compromise the natural barrier against bacteria, potentially leading to periodontal diseases that may damage the supporting bone structure and, in severe cases, result in tooth loss.
The process is often gradual and may not be noticeable until there is significant sensitivity or visible root exposure. Regular dental check-ups are essential to catch and manage gum recession early, preventing further complications and maintaining oral health.
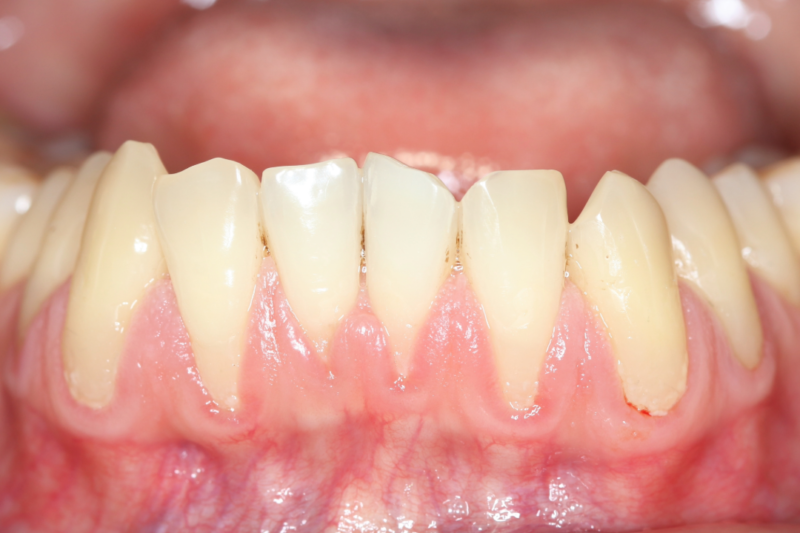
Causes of gum recession
Receding gums can be caused by a variety of factors, some within your control and others not so much. Here’s a rundown of the main reasons why someone might experience gum recession:
Genetics: Just like other parts of your body, the characteristics of your gums can be inherited. If your family has a history of gum disease or receding gums, you might be at a higher risk, even if you take good care of your teeth.
Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly can lead to plaque build-up on your teeth. Over time, this plaque turns into tartar, a hard substance that can only be removed by a dentist and can push your gums to recede.
Aggressive tooth brushing: If you brush your teeth too hard or use a toothbrush with stiff bristles, you might be harming your gums. Gentle brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush is recommended.
Periodontal diseases: Gum diseases, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, involve inflammation and infection of the gums and can destroy the support structures of your teeth, leading to gum recession.
Tobacco use: Smoking or chewing tobacco isn’t just bad for your lungs; it also affects your gums. Tobacco use can cause your gums to weaken and recede.
Hormonal changes: Significant changes in hormone levels during events like pregnancy or menopause can make gums more sensitive and more vulnerable to recession.
Knowing these factors can help you understand the possible risks and take steps to protect your gums, such as maintaining good oral hygiene, using the right toothbrush, and regularly visiting the dentist.
Receding gums stages
Understanding the stages of gum recession can help in early detection and treatment:
Mild: Slight exposure of the tooth root, often without symptoms.
Moderate: Increased exposure with some sensitivity or discomfort.
Severe: Significant root exposure, leading to severe pain, sensitivity, and higher risk of root decay and tooth loss.
Preventing receding gums
Preventing receding gums is crucial for maintaining good oral health. To protect your gums, it's important to adhere to a few key practices. First and foremost, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential. This means using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth gently twice a day, alongside daily flossing to remove plaque from areas your toothbrush can't reach.
Regular dental checkups are also vital. Visiting your dentist every six months allows for professional cleanings that remove tartar build-up, and provides an opportunity to catch any early signs of gum recession.
Another significant step is to quit smoking. Stopping tobacco use can greatly reduce the risk of further damage to your gums. Additionally, eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids supports healthy gums.
Finally, using therapeutic mouthwashes can be beneficial. These antimicrobial solutions help to reduce plaque and inflammation, further protecting your gums from recession. By integrating these practices into your daily routine, you can significantly enhance your gum health and prevent the progression of gum recession.
Treatments for receding gums
If you're experiencing gum recession, several treatment options are available to help manage and possibly reverse the condition, depending on its severity:
Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing)
This procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gumline, which helps prevent further gum recession and improves gum health.
Gum graft surgery
This involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth, typically the roof, and grafting it onto the areas where the gums have receded. This procedure covers exposed roots, reduces sensitivity, and protects the roots from decay.
Pinhole surgical technique
A minimally invasive option that involves making a small hole in the existing gum tissue. Special instruments are then used to gently loosen and reposition the gum over the exposed tooth roots. This technique offers immediate cosmetic improvements and root protection.
Regenerative procedures
Suitable for cases where the bone supporting the teeth has been compromised. These procedures involve placing regenerative materials such as grafts, membranes, or tissue-stimulating proteins to encourage the natural regeneration of bone and tissue in the affected area.
Each treatment option is chosen based on the severity of the gum recession and the overall health of your gums. Your dentist will determine the most appropriate treatment to ensure you receive the best care for your needs. Regular dental check-ups are crucial to monitor the health of your gums and adjust the treatment plan as necessary.
Conclusion
Receding gums can be a worrying condition, but you can manage and often reverse the damage with proper care and early intervention. Remember, the key to preventing gum recession is maintaining good oral hygiene, making informed lifestyle choices, and seeking regular professional dental care. By understanding the causes, recognising the stages, and adopting effective treatment strategies, you can ensure that your gums and teeth remain healthy for years to come.
Stay proactive about your dental health and consult your dentist if you notice any signs of gum recession. Early detection and treatment are crucial for maintaining your oral health and overall well-being.
Frequently asked questions - Receding gums
1. Can you fix receding gums?
Yes, receding gums can often be treated effectively. Treatments vary from deep cleanings to more intensive procedures like gum grafts or the Pinhole Surgical Technique, depending on the severity of the recession.
2. Why are my gums receding in my 20s?
Gum recession in your 20s can be caused by several factors, including aggressive brushing, poor dental hygiene, genetic predisposition, or the early onset of gum disease. Lifestyle factors such as smoking can also contribute.
3. Can you push receding gums back?
Gums cannot be "pushed back" to their original position once they have receded. However, treatments like gum grafts can cover the exposed roots and restore the gum line effectively.
4. Why is my gum receding around one tooth?
Gum recession around a single tooth can be caused by several factors, including localised periodontal disease, aggressive brushing techniques, trauma to the gum tissue, an uneven bite, or excessive pressure from habits like teeth clenching. Additionally, an improperly fitted dental restoration such as a crown or filling can also lead to recession. It’s important to consult with a dentist to identify the specific cause and receive appropriate treatment.
5. What does gum recession look like?
Gum recession typically appears as the lowering or pulling back of the gum tissue on the teeth, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. You might notice that your teeth look longer than usual or see a notch where the gum meets the tooth. This can sometimes be accompanied by increased sensitivity, especially to hot or cold temperatures. If you observe any of these changes, it’s advisable to consult a dentist for an evaluation.
